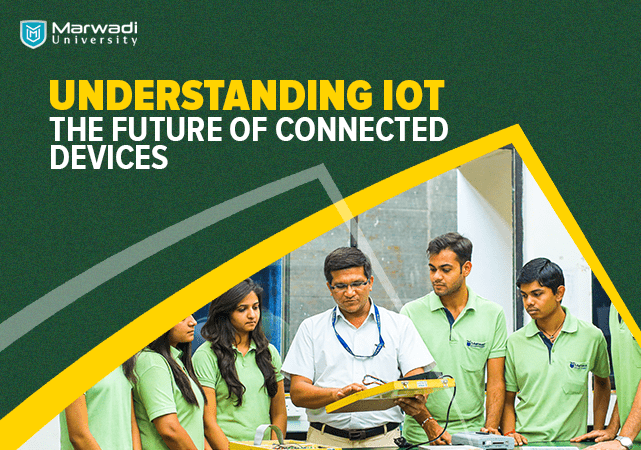
IoT (Internet of Things) is the interconnection of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other objects to the Internet. It has become increasingly important in the digital age due to its ability to collect and transmit data, enabling more efficient and effective decision-making.
The concept of IoT began in the 1980s with the first internet-connected device, but it wasn’t until the 2000s that the term was coined. Since then, IoT has evolved to include a vast range of connected devices and has become a key component of digital transformation in many industries.
Components of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) has four main components: sensors and actuators, connectivity, data processing and analytics, and user interfaces.
Sensors and Actuator: are the eyes and hands of the IoT system, respectively. Sensors detect and measure physical changes, while actuators respond to those changes by performing specific actions.
Connectivity: enables IoT devices to communicate with each other and with other systems. This includes technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks.
Data Processing and Analytics involve: collecting and analysing the data generated by IoT devices. This helps to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies, which can then be used to optimize performance, reduce costs, and improve safety.
User Interfaces: are how people interact with IoT devices. These can take many forms, such as mobile apps, web dashboards, voice assistants, or augmented reality interfaces.
These components work together to enable IoT systems to collect, analyse, and act on data in real time. Thus, making them valuable tools for a wide range of applications, from smart homes and cities to industrial automation and healthcare.
Applications of IoT
Smart homes and cities: IoT can be used in smart homes to automate processes like lighting, temperature, and security. In smart cities, it can be used for traffic management, waste management, and energy conservation.
Industrial IoT (IIoT): IIoT can help factories and industries to monitor and optimize their processes, track inventory, and perform predictive maintenance.
Healthcare: IoT can be used in healthcare for remote monitoring, patient care, and medication management.
Agriculture: IoT can help farmers monitor soil conditions, crop growth, and irrigation systems to improve crop yields and reduce water usage.
Transportation and Logistics: IoT can be used to optimize routes, monitor vehicle performance, and track shipments in real time, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Advantages and Challenges of IoT
Advantages
Improved efficiency and productivity: IoT enable automation and optimization of various processes, reducing the need for manual intervention. This can improve efficiency and productivity by reducing errors, streamlining workflows, and increasing the speed of operations.
Enhanced customer experience: IoT can help companies provide a more personalized and seamless customer experience. For example, by using IoT devices to gather data on customer preferences and behaviour, companies can tailor their products and services to better meet customer needs.
Improved decision-making: IoT generates large amounts of data that can be used to gain insights and make informed decisions. By analyzing this data, companies can identify patterns and trends, predict outcomes, and make data-driven decisions.
Challenges
Security and Privacy Concerns: IoT devices are vulnerable to security breaches, which can result in data theft, device hijacking, and other cyber-attacks. Additionally, the collection and use of personal data by IoT devices raise privacy concerns.
Integration and Compatibility issues: IoT devices often use different protocols and standards, which can make it difficult to integrate them with other systems. This can create compatibility issues and result in interoperability problems.
Complexity: IoT systems can be complex, with multiple devices, sensors, and networks involved. Managing and maintaining these systems can be challenging and requires specialized knowledge and expertise.
Future of IoT
The future of IoT is promising, with rapid growth and adoption predicted globally. IoT technology is evolving, with emerging trends such as edge computing and AI integration. These trends will enable more efficient and intelligent data processing, as well as improved security measures.
IoT has already played a significant role in shaping the digital economy, and it will continue to do so by facilitating automation, innovation, and enhanced customer experiences. As more industries and businesses implement IoT solutions, the benefits of the technology will become even more apparent.
Conclusion
If you’re curious about the Internet of Things (IoT), Marwadi University’s course is the perfect starting point! This program covers everything you need to know about IoT, from the basics to the advanced concepts. You’ll learn about IoT’s history, the technology behind it, and its applications in various industries.
The course’s experienced instructors provide you with practical experience by working on real-world IoT projects. You’ll also have access to the latest tools and technologies to build your IoT applications. This course is a fantastic opportunity to gain valuable knowledge and skills in IoT.















 International Airport
International Airport  Railway Station
Railway Station  GSRTC Bus Port
GSRTC Bus Port 


